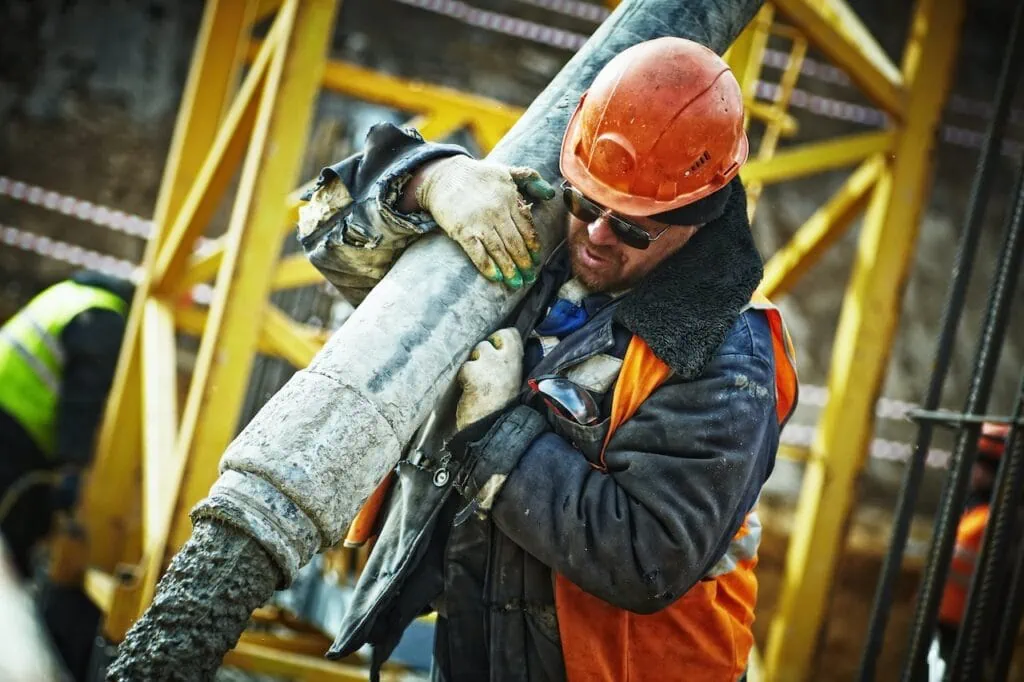
Workplace Injuries, Opioids and Addiction
Many people who work in high-stress environments also use substances recreationally, including opioids. Many people with opioid use disorder started with legal prescriptions due to workplace injuries. Some people end up misusing opioids or developing a tolerance to drugs they are taking and have trouble ceasing use once they’ve started. This can lead to opioid use disorder and a vicious, painful cycle of addiction. Certain industries are at higher risk than others for substance abuse and opioid addiction.
How Can Workplace Injuries Lead to Addiction?
Workplace injuries can increase the risk of opioid addiction because individuals who experience physical pain or injuries often end up prescribed opioids for recovery. This is especially true if the damage requires surgery. In addition, longer-term opioid use can lead to physical dependence and opioid use disorder, a disease of the brain that drives addiction. Workplace injuries also can lead to long-term disability and financial stress, contributing to substance misuse.
Healthcare providers have a role in helping people with workplace injuries recover safely. Treating workplace injuries should involve a multifaceted approach and prioritizing safe and responsible pain management practices. Physical therapy, neurological medications such as anticonvulsants, and other treatments are often more effective than opioids. People who take opioids for injuries individuals must also be taught the potential risks associated with opioid use.
Which Industries Are at Highest Risk for Opioid Use?
According to data from the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS), specific industries have higher rates of workplace injuries and illnesses than others. Opioid use disorder and substance use disorder are also high in these industries as well. The following sectors have historically had some of the highest rates of injury and substance use:
- Construction: Construction workers are at high risk for falls, electrical accidents, and other dangerous incidents. Everyday wear and tear also can cause repetitive stress injuries and osteoarthritis.
- Manufacturing: The physical demands of manual labor in manufacturing can lead to musculoskeletal disorders and other types of injury. Long hours on the job can also lead to boredom and isolation. Manufacturing as an industry has the highest rates of substance use.
- Agriculture: Agricultural workers face many hazards, including working with heavy machinery and exposure to harmful chemicals. Chronic health issues and pain can often result from injuries or illnesses. In rural communities, 74% of people say they know somebody affected by opioid misuse in the farming industry; 26% of farmers admit to misusing opioids or taking them without a prescription.
- Transportation and Warehousing: Workers in these industries risk injury from vehicle accidents and handling heavy loads. Long-haul truckers are often isolated from others and face workplace injuries from long hours on the road.
- Healthcare and social assistance: Healthcare workers face physical risk at work, including assaults from patients and on-the-job injuries. Many healthcare workers also face psychological stress due to healthcare shortages. COVID has only increased the pressure on many workers.
These are just a few examples of industries with high rates of injury. In addition, these industries are likely to have people who live with increased rates of stress and may live in communities that are more at risk for substance use disorder.
Getting Help for Addiction
While these industries are at higher risk for opioid use, individuals from all walks of life can be affected by addiction. If you or somebody you love is living with opioid use disorder, we can help you get sober! Learn more about our programs and how we help.
Categories
Addiction